MAC Overview
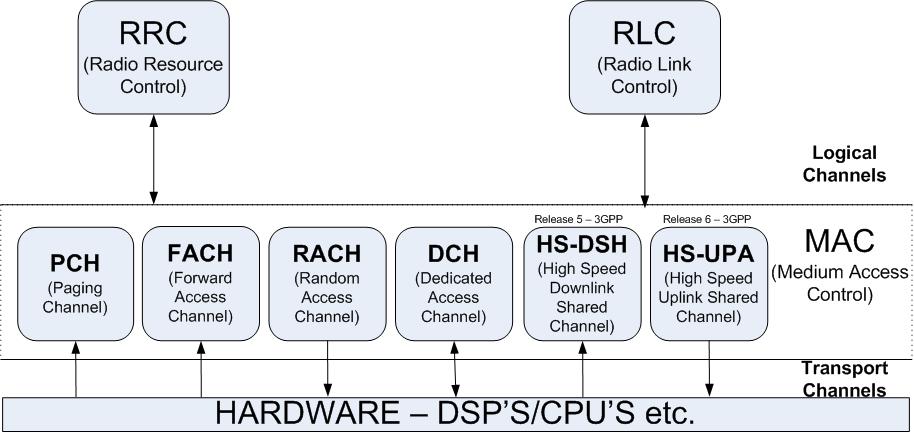
MAC Overview
MAC (Medium Access Control) Overview
- Mapping between logical and transport channels
- Selection of appropriate transport formats for each channel
- Uses RRC’s (Radio Resource Control) instruction to choose the correct transport format, depending on factors such as buffer occupancy, UL transmit power, and logical channel priority. Control means better control of transport channels. More about Transport Channels can be found here.
- Priority handling between data flows from the UE (User Equipment)
- Identifications of UE’s on common transport channels
- Multiplexing/demultiplexing of upper layer PDU’s into/from transport blocks delivered to/from the physical layer on common transport and dedicated channels.
- Traffic volume measurement – measured on logical channels, measured and reported back to the RRC. Based on the reported traffic volume information, the RRC makes transport channel switching decisions.
- Execution of the switching between common and dedicated transport channels based on a switching decision initiated by RRC
- Ciphering
- Access service class selection for RACH transmission.
Transport channel
The channels that are offered by the physical layer to Layer 2 for data transport between peer L1 entities are denoted as Transport Channels.
Different types of transport channels are defined by how and with which characteristics data is transferred on the physical layer, e.g. whether using dedicated or common physical channels are employed.
- PCH (Paging Channel)
- is a downlink transport channel that is used to carry control information to a mobile station when the system does not know the location cell of the mobile station. The PCH is always transmitted over the entire cell. It also waits for a phone call.
- In idle mode, the mobile station uses a sleep mode that permits that e.g. most of the circuits can be turned off during the periods when the mobile station is not receiving. The mobile station is only awakened for short periods to listen to e.g. the paging channel or the broadcast channel.
- characterised by:
- existence in downlink only,
- possibility for sleep mode procedures and
- requirement to be broadcast in the entire coverage area of the cell.
- FACH (Forward Access Channel)
- is a downlink transport channel that is used to carry control information to a mobile station when the system knows the location cell of the mobile station. The FACH may also carry short user packets. The FACH is transmitted over the entire cell or over only a part of the cell using lobe-forming antennas.
-
- characterised by:
- existence in downlink only,
- possibility to use beam-forming,
- possibility to use slow power control,
- lack of fast power control and
- requirement for in-band identification of MSs.
- RACH (Random Access Channel
- when it needs to get the attention of a base station in order to initially synchronize its transmission with the base station.
- Random Access Channel is a shared channel that is used by Wireless Access terminals to Access the Access Network especially for initial Access and Bursty data transmission.
- A key feature of a Random Access Channel is that messages are not scheduled (compared to for example a "Dedicated Channel" in UMTS, that is assigned exclusively to one user at a time). There is no certainty, that only a single device makes a connection attempt at one time, and collisions can result.
-
- DCH (Dedicated Transport Channel)
- is a downlink or uplink transport channel that is used to carry user or controlinformation between the network and a mobile station. The DCH thus corresponds to the three channels
- Dedicated Traffic Channel (DTCH),
- Stand-alone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH),
- and Associated Control Channel (ACCH) defined within ITU-R M.1035. The DCH is transmitted over the entire cell or over only a part of the cell using lobe-forming antennas.
- HS-DSCH (High Speed Downlink Shared Channel)
- is used in HSDPA (UMTS) to send packets on the downlink to the UEs. It is called High-Speed to distinguish it from the more general definition of the downlink shared channel (DSCH) in UMTS. (The latter channel is sometimes referred to as Release'99 DSCH.)
- HS-USCH (High Speed Uplink Shared Channel)

